Part X
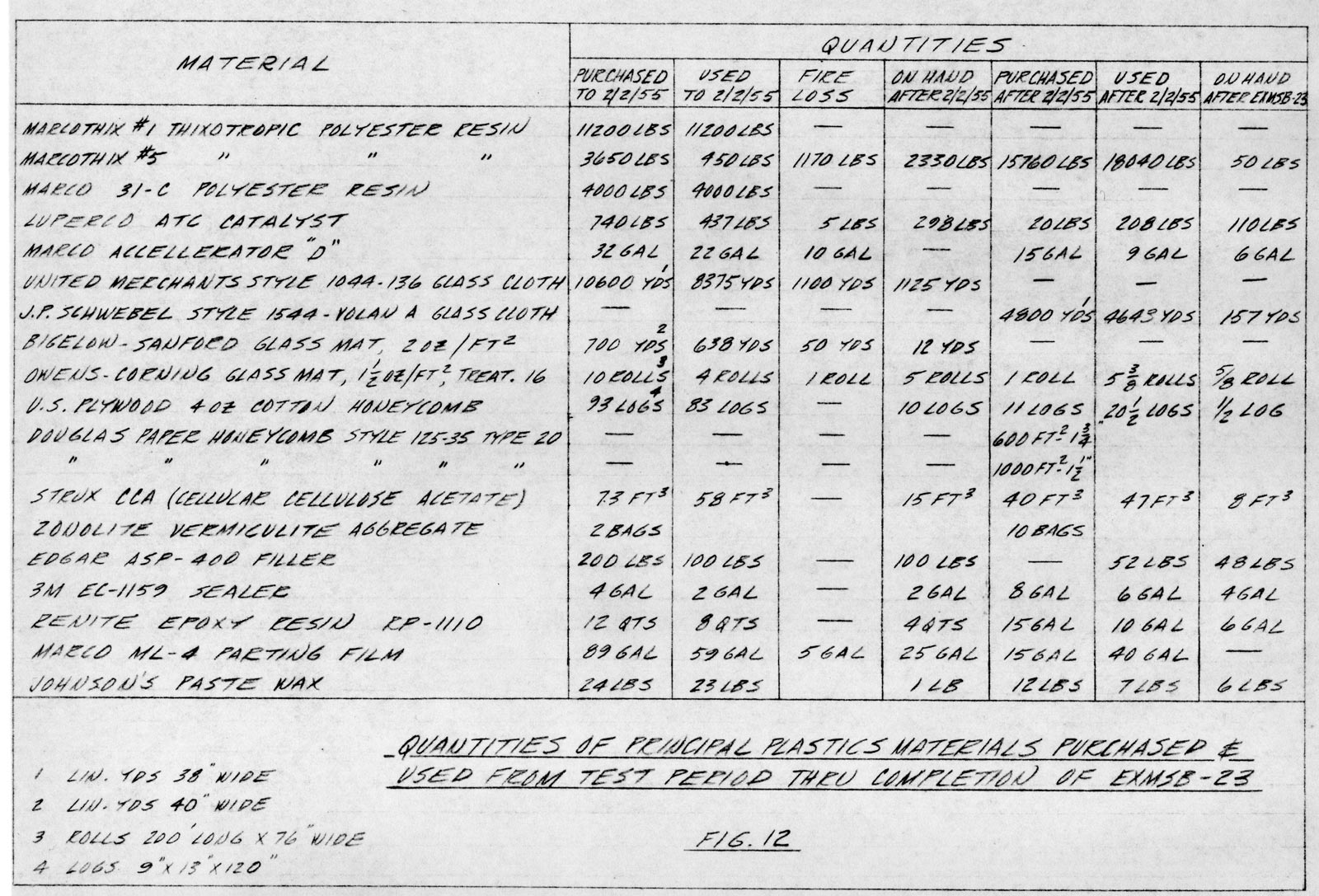
Materials
Materials
Preimpregnated Glass Cloths
Sources:
Fabricon Products, Inc., River Rouge, Michigan
Gordo Molding Products, Inc., 230 Park Ave., New York 17, New York
Electro-Technical Products Div., Sun Chemical Corp. (Sunform)
Discussion:
Preimpregnated cloths were cured under vacuum bag pressure and at temperatures from 180°F to 250°F. Fabricon pre-pregs were used for all 3"x16" test panels, many of the 5"x20" panels, and two 99" square panels for testing by the New York Naval Shipyard. Gordo pre-pregs were used in many of the 5"x20" test panels and in one 99" square panel for NYNSY. Sunform pre-pregs were used in a small number of 5"x20" panels.
Preimpregnated cloths generally were superseded by thixotropic resins and wet layup procedures.
Low Density Core Materials
Sources:
Dow Chemical Co., Midland, Michigan
Styrofoam #22 unicellular expanded polystyrene
Western Products, Inc., Newark, Ohio
1/4" cell size glass honeycomb BFP 3.5
Chrysler Corporation, Detroit, Michigan
Paper honeycomb, 1/2" cell size, "ribbon candy" type
Douglas Aircraft Corporation, Santa Monica, Calif.
Style 60-20 type 40 paper honeycomb, 3/8" cell size
Style 60-20 type 30 paper honeycomb, 3/8" cell size
Style 125-35 type 20 paper honeycomb, 3/8" cell size
Lincoln Industries, Marion, Va.
Paper honeycomb, polyester impregnated
Paper honeycomb, untreated
U. S. Plywood Corp., New York, N. Y.
Later - Honeycomb Corp. of America
4 oz. cotton honeycomb phenolic impregnated
Strux Corporation, Lindenhurst, L. I., N. Y.
C.C.A. (Cellular Cellulose Acetate) 6-7 lbs/ft³
Discussion:
Dow styrofoam was used in a few 3"x16" test panels, but low softening temperature and solubility in polyester resins caused rejection in favor of other core materials.
Western Products glass honeycomb was very expensive and proved subject to shattering under impact.
Chrysler paper honeycomb was used in a few 3"x16" test panels. Its untreated nature indicated unsuitability for marine work.
Douglas paper honeycombs were used in some 5"x20" test panels but were passed up for use in MSB-23 in favor of cotton honeycomb.
The style 125-35 type 20 paper honeycomb was used in ExMSB-23 for the deck, bulwarks and hull above the waterline.
Lincoln paper honeycombs were used in a few 3"x16" test panels only. They proved excessively brittle.
U. S. Plywood cotton honeycombs were used for most of the 5"x20" test panels, all the 99" square panels for NYNSY, and all the 9"x60" test panels. This honeycomb was used exclusively on MSB-23 and on ExMSB-23 below the waterline.
Strux C.C.A. was used as a core material in those instances where compound curvature was not a factor. This included keel, deck beams, studs, and internal reinforcement of the hull, shaft logs, and strut clamps.
Glass Reinforcements
Sources:
United Merchants Industrial Fabrics, New York, N.Y.
Style 1000 cloth, 136 finish, 44" wide
Style 1044 cloth, 136 finish, 38" wide
J. P. Schwebel, New York, N.Y.
Style 1544 cloth, Volan-A finish, 38" wide
Owens Corning Fiberglas, Toledo, Ohio
1½ oz/ft² mat, treatment 16 (soluble polyester binder)
1/4" milled fibers, cationic binder
Bigelow-Sanford Carpet Co., Inc., New York, N.Y.
2 oz mat, 40" wide
Ferro Corp., Fiberglass Division, Nashville, Tenn.
1½ oz uniform mat
Hess-Goldsmith & Co., Inc., New York, N.Y.
X561/H₂ woven rovings, 1000×900
X563/H₂ woven rovings, 1000×500
X568/H₂ woven rovings, 1000×50
Discussion:
U. M. Style 1000 cloth was used for some early practice layups and 9"x60" panels. It was superseded by style 1044-136 cloth which gave a more rapid laminate buildup because of its greater thickness. 1044-136 cloth was used for most of the 9"x60" test panel program and for all laminates in MSB-23 including bulkheads, girders and other pre-fabrications. Part of the inner skin of ExMSB-23 was laid up with 1044-136 cloth.
J. P. Schwebel's style 1544 cloth with the Volan-A finish was used for all further laminating on ExMSB-23. Lower cost plus the superiority of the Volan-A finish over 136 were the reasons for adopting the 1544 cloth.
Owens-Corning 1½ oz mat was used as a bonding layer in many of the 9"x60" panels as well as for all major sandwich panels on both MSB-23 and ExMSB-23. 1/4" milled fibers were tried in conjunction with resin as a bonding medium and were used as a filler in miscellaneous instances.
Bigelow-Sanford mat was used in one 99" square panel for New York Naval Shipyard and in the female mold shell for MSB-23. It was not used as a bonding medium because the 2 oz weight was the lightest available and weight saving was an important consideration.
Ferro 1½ oz/ft² mat was used in a few 9"x60" test panels. No improvement was noted over Owens-Corning 1½ oz mat.
Hess-Goldsmith woven rovings were used as laminating reinforcements and bonding plies in some of the 9"x60" test panels. They did not prove superior as bonding media. Panels using the woven roving laminates proved far stronger than those made with conventional cloths.
The material was not then available in sufficient quantity to allow its use in MSB-23.
Resins
Sources:
Marco Chemical Co., Linden, N. J.
Later - Celanese Corp., Newark, N. J.
Marcothix #1 thixotropic resin
Marco TC-24-1 thixotropic resin
Marcothix #5 thixotropic resin
Marco 31-C low-exotherm resin
Marco 30-C flexible resin
Marco 28-C general purpose resin
Interchemical Corporation
IC-706 Non air inhibited resin
Ren Plastics, Lansing, Michigan
Renite RP-1110 epoxy resin
Discussion:
Luperco ATC catalyst was used in conjunction with Marco's accelerator "D" in activating all thixotropic resins and mixtures.
Marco MC-1 catalyst and accelerator "E" were used with Marco 28-C resin only.
Fillers
Sources:
J. W. Stark Co., Detroit, Mich.
Edgar ASP-400 filler, aluminum silicate
Zonolite Co., Chicago, Ill.
Vermiculite aggregate
Discussion:
Edgar ASP filler was used with Marcothix resin in a 30%-70% mixture for injected thru-bolt bosses in sandwich panels.
Vermiculite aggregate was used with Marcothix resin in a 20%-80% mixture for void-filling applications including thru-bolt areas.
Sealers
Sources:
Ren Plastics, Lansing, Mich.
Renite RP-802 sealer
Dupont
Duco clear lacquer
Minnesota Mining & Mfg. Co., Inc.
3M-EC-1159 Sealer
Discussion:
Renite RP-802 sealer was used on the plaster male plug of the practice bow section.
Duco clear lacquer was used to seal the plaster surface of the male mold plug for MSB-23 and the plywood deck mold for ExMSB-23.
EC-1159 sealer was used in sealing all thru-bolts and stuffing tubes in ExMSB-23. It was also used in bedding strut palms and thru-hull fittings on ExMSB-23.
Parting Agents
Sources:
Ren Plastics, Lansing, Michigan
Renite RP-801 Parting Film
S. C. Johnson & Son, Racine, Wisconsin
Johnson's Paste Wax
Celanese Corporation, Newark, N. J.
Marco ML-4 Parting Film
Discussion:
Renite's RP-801 parting film was used on the male plug of the practice bow section mold project.
Johnson's Paste Wax was used in conjunction with Marco's ML-4 parting film for all major mold-parting applications, including bench and table layups, for both MSB-23 and ExMSB-23.
Surfacing Films
Sources:
Reynolds Metals Co., Gary, Indiana
Polyvinyl alcohol film
Various sources:
Cellophane film
Discussion:
PVA film was used over all laminates except major hull laminates as an air-excluding surfacing film and as a means for isolating wet layups from vacuum bagging bleeders and blankets.
Cellophane was used similarly but its use was generally limited to small bench layups.
Vacuum Bag Material
Source:
Firestone Plastics, Pottstown, Penn.
Velon polyvinyl chloride film .004" thick
Discussion:
Velon film was used as the vacuum blanket material for all fabrications on both MSB-23 and ExMSB-23.
PVA was used during the early research period in bagging panels laid up with pre-pregs.